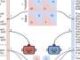
In biomedical research, so-called organs-on-a-chip, also referred to as microphysiological systems, are becoming increasingly important: by cultivating tissue structures in precisely controlled microfluidic chips, it is possible to conduct research much more accurately than in experiments involving living humans or animals. These systems can be used to investigate the effects of a new drug and to better understand the interaction between different organs to grasp the systemic response.
© 2024 EarnWithSocial.ca - Canada's Technology News and Highlights | Read. Learn. Share.